-

新人教版高中英语选修2Unit 5 Learning about Language教学设计
The purpose of this section of vocabulary exercises is to consolidate the key words in the first part of the reading text, let the students write the words according to the English definition, and focus on the detection of the meaning and spelling of the new words. The teaching design includes use English definition to explain words, which is conducive to improving students' interest in vocabulary learning, cultivating their sense of English language and thinking in English, and making students willing to use this method to better grasp the meaning of words, expand their vocabulary, and improve their ability of vocabulary application. Besides, the design offers more context including sentences and short passage for students to practice words flexibly.1. Guide students to understand and consolidate the meaning and usage of the vocabulary in the context, 2. Guide the students to use the unit topic vocabulary in a richer context3. Let the students sort out and accumulate the accumulated vocabulary, establishes the semantic connection between the vocabulary,4. Enable students to understand and master the vocabulary more effectivelyGuiding the Ss to use unit topic words and the sentence patterns in a richer context.Step1: Read the passage about chemical burns and fill in the blanks with the correct forms of the words in the box.

新人教版高中英语选修2Unit 3 Reading for writing教学设计
The theme of this part is to write an article about healthy diet. Through reading and writing activities, students can accumulate knowledge about healthy diet, deepen their understanding of the theme of healthy diet, and reflect on their own eating habits. This text describes the basic principles of healthy diet. The author uses data analysis, definition, comparison, examples and other methods. It also provides a demonstration of the use of conjunctions, which provides important information reference for students to complete the next collaborative task, writing skills, vivid language materials and expressions.1. Teach Ss to learn and skillfully use the new words learned from the text.2. Develop students’ ability to understand, extract and summarize information.3. Guide students to understand the theme of healthy diet and reflect on their own eating habits.4. To guide students to analyze and understand the reading discourse from the aspects of theme content, writing structure, language expression, etc., 5. Enable Ss to write in combination with relevant topics and opinions, and to talk about their eating habits.1. Guide students to analyze and understand the reading discourse from the aspects of theme content, writing structure, language expression, etc.2. Enable them to write in combination with relevant topics and opinions, and to talk about their eating habits.3. Guide the students to use the cohesive words correctly, strengthen the textual cohesion, and make the expression fluent and the thinking clear.Step1: Warming upbrainstorm some healthy eating habits.1.Eat slowly.2.Don’t eat too much fat or sugar.3.Eat healthy food.4.Have a balanced diet.Step2: Read the passage and then sum up the main idea of each paragraph.

新人教版高中英语选修2Unit 3 Using langauge-Listening教学设计
1. How is Hunan cuisine somewhat different from Sichuan cuisine?The heat in Sichuan cuisine comes from chilies and Sichuan peppercorns. Human cuisine is often hotter and the heat comes from just chilies.2.What are the reasons why Hunan people like spicy food?Because they are a bold people. But many Chinese people think that hot food helps them overcome the effects of rainy or wet weather.3.Why do so many people love steamed fish head covered with chilies?People love it because the meat is quite tender and there are very few small bones.4.Why does Tingting recommend bridge tofu instead of dry pot duck with golden buns?Because bridge tofu has a lighter taste.5 .Why is red braised pork the most famous dish?Because Chairman Mao was from Hunan, and this was his favorite food.Step 5: Instruct students to make a short presentation to the class about your choice. Use the example and useful phrases below to help them.? In groups of three, discuss what types of restaurant you would like to take a foreign visitor to, and why. Then take turns role-playing taking your foreign guest to the restaurant you have chosen. One of you should act as the foreign guest, one as the Chinese host, and one as the waiter or waitress. You may start like this:? EXAMPLE? A: I really love spicy food, so what dish would you recommend?? B: I suggest Mapo tofu.? A: Really ? what's that?

新人教版高中英语选修2Unit 4 Learning about Language教学设计
This section guides students to pay attention to the typical context of vocabulary use, helps students accumulate vocabulary around the key vocabulary of this unit, and uses the learned words and word chunks in different contexts to deeply understand their meaning and usage, so as to achieve the purpose of review and consolidation.The teaching design activities aim to guide students to pay attention to the typical context in which the target vocabulary is used, as well as the common vocabulary used in collocation, so that students can complete the sentence with correct words. In terms of vocabulary learning strategies, this unit focuses on cultivating students' ability to pay attention to collocation of words and to use word blocks to express meaning.For vocabulary learning, it is not enough just to know the meaning of a single word, but the most important thing is to master the common collocations of words, namely word blocks.Teachers should timely guide students to summarize common vocabulary collocation, such as verb and noun collocation, verb and preposition collocation, preposition and noun collocation, and so on.1. Guide students to understand and consolidate the meaning and usage of the vocabulary in the context, 2. Guide the students to use the unit topic vocabulary in a richer context3. Let the students sort out and accumulate the accumulated vocabulary, establishes the semantic connection between the vocabulary,4. Enable students to understand and master the vocabulary more effectivelyGuiding the Ss to use unit topic words and the sentence patterns in a richer context.

新人教版高中英语选修2Unit 4 Using langauge-Listening教学设计
The theme of the listening section is " talking about scenery and culture along a journey."The part is designed to further lead the students to understand Canadian natural geography and social environment, and integrated into the cultural contrast by mentioning the long train journey from Beijing to Moscow routes. On this basis, the part activates students related travel experience, lets the student serial dialogue, guides the student to explore further the pleasure and meaning of the long journey, and Chinese and foreign cultural comparison.The part also provides a framework for the continuation of the dialogue, which is designed to provide a framework for students to successfully complete their oral expressions, and to incorporate an important trading strategy to end the dialogue naturally.1. Help students to understand and master some common English idioms in the context, and experience the expression effect of English idioms.2. Guide the students to understand the identity of different people in the listening context, and finish the dialogue according to their own experience.3. Instruct the students to use appropriate language to express surprise and curiosity about space and place in the dialogue, and master the oral strategy of ending the dialogue naturally.1. Instruct students to grasp the key information and important details of the dialogue.2. Instruct students to conduct a similar talk on the relevant topic.
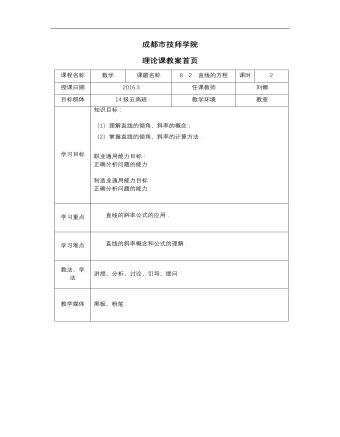
高教版中职数学基础模块下册:8.2《直线的方程》教学设计
课程名称数学课题名称8.2 直线的方程课时2授课日期2016.3任课教师刘娜目标群体14级五高班教学环境教室学习目标知识目标: (1)理解直线的倾角、斜率的概念; (2)掌握直线的倾角、斜率的计算方法. 职业通用能力目标: 正确分析问题的能力 制造业通用能力目标: 正确分析问题的能力学习重点直线的斜率公式的应用.学习难点直线的斜率概念和公式的理解.教法、学法讲授、分析、讨论、引导、提问教学媒体黑板、粉笔

北师大初中八年级数学下册三角形的全等和等腰三角形的性质教案
证明:过点A作AF∥DE,交BC于点F.∵AE=AD,∴∠E=∠ADE.∵AF∥DE,∴∠E=∠BAF,∠FAC=∠ADE.∴∠BAF=∠FAC.又∵AB=AC,∴AF⊥BC.∵AF∥DE,∴DE⊥BC.方法总结:利用等腰三角形“三线合一”得出结论时,先必须已知一个条件,这个条件可以是等腰三角形底边上的高,可以是底边上的中线,也可以是顶角的平分线.解题时,一般要用到其中的两条线互相重合.三、板书设计1.全等三角形的判定和性质2.等腰三角形的性质:等边对等角3.三线合一:在等腰三角形的底边上的高、中线、顶角的平分线中,只要知道其中一个条件,就能得出另外的两个结论.本节课由于采用了动手操作以及讨论交流等教学方法,有效地增强了学生的感性认识,提高了学生对新知识的理解与感悟,因而本节课的教学效果较好,学生对所学的新知识掌握较好,达到了教学的目的.不足之处是少数学生对等腰三角形的“三线合一”性质理解不透彻,还需要在今后的教学和作业中进一步巩固和提高

北师大初中九年级数学下册直线和圆的位置关系及切线的性质教案
解析:(1)由切线的性质得AB⊥BF,因为CD⊥AB,所以CD∥BF,由平行线的性质得∠ADC=∠F,由圆周角定理的推论得∠ABC=∠ADC,于是证得∠ABC=∠F;(2)连接BD.由直径所对的圆周角是直角得∠ADB=90°,因为∠ABF=90°,然后运用解直角三角形解答.(1)证明:∵BF为⊙O的切线,∴AB⊥BF.∵CD⊥AB,∴∠ABF=∠AHD=90°,∴CD∥BF.∴∠ADC=∠F.又∵∠ABC=∠ADC,∴∠ABC=∠F;(2)解:连接BD,∵AB为⊙O的直径,∴∠ADB=90°,∴∠A+∠ABD=90°.由(1)可知∠ABF=90°,∴∠ABD+∠DBF=90°,∴∠A=∠DBF.又∵∠A=∠C,∴∠C=∠DBF.在Rt△DBF中,sin∠DBF=sinC=35,DF=6,∴BF=10,∴BD=8.在Rt△ABD中,sinA=sinC=35,BD=8,∴AB=403.∴⊙O的半径为203.方法总结:运用切线的性质来进行计算或论证,常通过作辅助线连接圆心和切点,利用垂直构造直角三角形解决有关问题.

人教版新课标小学数学五年级下册分数的意义和性质教案
6. 本题是一道实际应用的题,可以结合生活实际举例,在举例中进一步认识分数。7. (读作八分之一)表示把人的身高看作单位“1”,头部的高度占整个身高的 ; (读作五分之三)表示把整个长江的干流看作单位“1”,受污染的部分占整个长江干流的 ; (读作十分之三)表示把死海表层的水看作单位“1”,含盐量占死海表层水的 。8. 读作六分之一, 读作七分之二, 读作是十五分之四, 读作十八分之十一, 读作一百分之七。它们的分数单位分别是: 、 、 、 、 。9. 本题有两个知识点:一是根据分数的意义涂色,是把12个苹果平均分成了2份,1份有6个苹果; 是把12个苹果平均分成了3份,1份有4个苹果; 是把12个苹果平均分成了4份,1份有3个苹果; 是把12个苹果平均分成了6份,1份有2个苹果; 是把12个苹果平均分成了12份,1份有1个苹果。二是在涂色中感受平均分成的份数越多,每一份越少,也可以说随着分母的增大,几分之一所表示的苹果个数,从 的6个到 的1个,相应地在减少。

小学数学人教版六年级下册《第二课比例的基本性质》教案说课稿
(一)观图激趣、设疑导入 师:上一节我们已经认识了比例,知道两个比怎样才能组成比例,下面请同学们判断一下下面各组的比能否组成比例。(1)0.4∶和1.2∶2 (2)和生1:根据比例的意义,第(1)题,这两个比的比值相等,都是0.6,所以(1)题的两个比能组成比例。生2:我来回答第(2)题,我也利用比例的意义,求出=5,=6,这两个比的比值不相等,所以第(2)题的两个比不能组成比例。师:这两名同学回答的真好,有理有据,让我们为他们的表现鼓掌!师:今天这节课,我们将共同来学习用另一种方法来判断两个比能否组成比例,同学们想知道是什么方法吗?生:想知道。师:那就是比例的基本性质(板书课题:比例的基本性质)。【设计意图】复习学生已有的知识,唤醒学生已有学习经验,教师的提问吸引了学生的注意力,也引发学生的好奇心,为学习新知识开了一个好头。

小学数学人教版六年级上册《比的基本性质》说课稿
一、说教材1、教材所处的地位和作用:《比的基本性质》是小学数学人教版六年级上册第三单元第三小节比和比的应用的第二课时。它是在学生学习商不变性质、分数的基本性质、比的意义、比和除法的关系、比和分数的关系的基础上组织教学的。比的基本性质是一节概念课的教学,它跟分数的基本性质、商不变性质实际上是同一道理的。所以本节课主要是处理新旧知识间的联系,在巩固旧知识的基础上进入到学习新知识。教材内容渗透着事物之间是普遍联系和互相转化的辩证唯物主义观点。学生理解并掌握比的基本性质,不但能加深对商不变性质、分数的基本性质、比的意义、比和分数、比和除法等知识的理解与掌握,而且也为以后学习比的应用,比例知识,正、反比例打好基础。

小学数学人教版六年级下册《比例的意义和基本性质》说课稿
1.说教材《比例的意义和基本性质》是人教版小学数学六年级下册第四单元的内容,这部分内容是在学习了比的有关知识并掌握了一些常见的数量关系的基础上进行教学的,是前面“比的知识”的深化,也是后面学习解比例知识的基础,并为学习比例的应用,特别是为正、反比例及其应用打好基础。比例的知识在生活和生产中有着广泛的应用,所以本节课的知识就显得尤为重要。2.教学目标我以《新课程标准》为依据,结合小学数学教材编排的意图和学生的实际情况,拟定以下教学目标:(1)知识与技能目标:使学生理解并掌握比例的意义和基本性质,认识比例各部分名称,知道比和比例的区别。(2)能力目标:培养学生自主参与的意识和主动探究的精神,培养学生初步的观察、分析、比较、判断、概括的能力,发展学生的思维。 (3)情感与态度目标:在教学中渗透爱国主义教育,培养学生善于观察、勤于思考、乐于探究的学习习惯。3.教学重点、难点教学重点:理解比例的意义与探究基本性质。教学难点:运用比例的意义或性质判断两个比能否组成比例,并能正确地组成比例。

北师大初中七年级数学上册等式的基本性质教案1
方法总结:对等式进行变形,必须在等式的两边同时进行,即同加或同减,同乘或同除,不能漏掉一边,且同加或同减,同乘或同除的数必须相同.探究点二:利用等式的基本性质解方程用等式的性质解下列方程:(1)4x+7=3; (2)12x-13x=4.解析:(1)在等式的两边都减7,再在等式的两边都除以4,可得答案;(2)在等式的两边都乘以6,再合并同类项,可得答案.解:(1)方程两边都减7,得4x=-4.方程两边都除以4,得x=-1;(2)方程两边都乘以6,得3x-2x=24,x=24.方法总结:解方程时,一般先将方程变形为ax=b的形式,然后再变形为x=c的形式.三、板书设计教学过程中,强调学生自主探索和合作交流,通过观察、操作、归纳等数学活动,感受数学思想的条理性和数学结论的严密性.

北师大初中八年级数学下册不等式的基本性质教案
【类型二】 根据不等式的变形确定字母的取值范围如果不等式(a+1)x<a+1可变形为x>1,那么a必须满足________.解析:根据不等式的基本性质可判断a+1为负数,即a+1<0,可得a<-1.方法总结:只有当不等式的两边都乘(或除以)一个负数时,不等号的方向才改变.三、板书设计1.不等式的基本性质性质1:不等式的两边都加上(或减去)同一个整式,不等号的方向不变;性质2:不等式的两边都乘(或除以)同一个正数,不等号的方向不变;性质3:不等式的两边都乘(或除以)同一个负数,不等号方向改变.2.把不等式化成“x>a”或“x<a”的形式“移项”依据:不等式的基本性质1;“将未知数系数化为1”的依据:不等式的基本性质2、3.本节课学习不等式的基本性质,在学习过程中,可与等式的基本性质进行类比,在运用性质进行变形时,要注意不等号的方向是否发生改变;课堂教学时,鼓励学生大胆质疑,通过练习中易出现的错误,引导学生归纳总结,提升学生的自主探究能力.

北师大初中八年级数学下册分式的基本性质教案
【类型二】 分式的约分约分:(1)-5a5bc325a3bc4;(2)x2-2xyx3-4x2y+4xy2.解析:先找分子、分母的公因式,然后根据分式的基本性质把公因式约去.解:(1)-5a5bc325a3bc4=5a3bc3(-a2)5a3bc3·5c=-a25c;(2)x2-2xyx3-4x2y+4xy2=x(x-2y)x(x-2y)2=1x-2y.方法总结:约分的步骤;(1)找公因式.当分子、分母是多项式时应先分解因式;(2)约去分子、分母的公因式.三、板书设计1.分式的基本性质:分式的分子与分母都乘以(或除以)同一个不为零的整式,分式的值不变.2.符号法则:分式的分子、分母及分式本身,任意改变其中两个符号,分式的值不变;若只改变其中一个符号或三个全变号,则分式的值变成原分式值的相反数.本节课的流程比较顺畅,先探究分式的基本性质,然后顺势探究分式变号法则.在每个活动中,都设计了具有启发性的问题,对各个知识点进行分析、归纳总结、例题示范、方法指导和变式练习.一步一步的来完成既定目标.整个学习过程轻松、愉快、和谐、高效.

北师大初中八年级数学下册旋转的定义和性质教案
(3)∵AD=4,DE=1,∴AE=42+12=17.∵对应点到旋转中心的距离相等且F是E的对应点,∴AF=AE=17.(4)∵∠EAF=90°(旋转角相等)且AF=AE,∴△EAF是等腰直角三角形.【类型二】 旋转的性质的运用如图,点E是正方形ABCD内一点,连接AE、BE、CE,将△ABE绕点B顺时针旋转90°到△CBE′的位置.若AE=1,BE=2,CE=3则∠BE′C=________度.解析:连接EE′,由旋转性质知BE=BE′,∠EBE′=90°,∴△BEE′为等腰直角三角形且∠EE′B=45°,EE′=22.在△EE′C中,EE′=22,E′C=1,EC=3,由勾股定理逆定理可知∠EE′C=90°,∴∠BE′C=∠BE′E+∠EE′C=135°.三、板书设计1.旋转的概念将一个图形绕一个顶点按照某个方向转动一个角度,这样的图形运动称为旋转.2.旋转的性质一个图形和它经过旋转所得的图形中,对应点到旋转中心的距离相等,任意一组对应点与旋转中心的连线所成的角都等于旋转角,对应线段相等,对应角相等.

北师大初中七年级数学下册角平分线的性质教案
解析:根据AB∥CD,∠ACD=120°,得出∠CAB=60°.再根据尺规作图得出AM是∠CAB的平分线,即可得出∠MAB的度数.解:∵AB∥CD,∴∠ACD+∠CAB=180°.又∵∠ACD=120°,∴∠CAB=60°.由尺规作图知AM是∠CAB的平分线,∴∠MAB=12∠CAB=30°.方法总结:通过本题要掌握角平分线的作图步骤,根据作图明确AM是∠BAC的角平分线是解题的关键.三、板书设计1.角平分线的性质:角平分线上的点到这个角的两边的距离相等.2.角平分线的作法本节课由于采用了动手操作以及讨论交流等教学方法,从而有效地增强了学生对角以及角平分线的性质的感性认识,提高了学生对新知识的理解与感悟,因而本节课的教学效果较好,学生对所学的新知识掌握较好,达到了教学的目的.不足之处是少数学生在性质的运用上还存在问题,需要在今后的教学与作业中进一步的加强巩固和训练

北师大初中七年级数学下册等腰三角形的性质教案
方法总结:在等腰三角形有关计算或证明中,会遇到一些添加辅助线的问题,其顶角平分线、底边上的高、底边上的中线是常见的辅助线.三、板书设计1.等腰三角形的性质:等腰三角形是轴对称图形;等腰三角形顶角的平分线、底边上的中线、底边上的高重合(也称“三线合一”),它们所在的直线都是等腰三角形的对称轴;等腰三角形的两个底角相等.2.运用等腰三角性质解题的一般思想方法:方程思想、整体思想和转化思想.本节课由于采用了直观操作以及讨论交流等教学方法,从而有效地增强了学生的感性认识,提高了学生对新知识的理解与感悟,因而本节课的教学效果较好,学生对所学的新知识掌握较好,达到了教学的目的.不足之处是少数学生对等腰三角形的“三线合一”性质理解不透彻,还需要在今后的教学和作业中进一步巩固和提高

北师大初中七年级数学下册线段垂直平分线的性质教案
解析:(1)根据AD∥BC可知∠ADC=∠ECF,再根据E是CD的中点可求出△ADE≌△FCE,根据全等三角形的性质即可解答;(2)根据线段垂直平分线的性质判断出AB=BF即可解答.解:(1)∵AD∥BC,∴∠ADC=∠ECF.∵E是CD的中点,∴DE=EC.又∵∠AED=∠CEF,∴△ADE≌△FCE,∴FC=AD;(2)∵△ADE≌△FCE,∴AE=EF,AD=CF.又∵BE⊥AE,∴BE是线段AF的垂直平分线,∴AB=BF=BC+CF.∵AD=CF,∴AB=BC+AD.方法总结:此题主要考查线段的垂直平分线的性质等几何知识.线段垂直平分线上的点到线段两个端点的距离相等,利用它可以证明线段相等.探究点二:线段垂直平分线的作图如图,某地由于居民增多,要在公路l边增加一个公共汽车站,A,B是路边两个新建小区,这个公共汽车站C建在什么位置,能使两个小区到车站的路程一样长(要求:尺规作图,保留作图痕迹,不写画法)?

北师大初中数学九年级上册位似多边形及其性质1教案
①分别连接OA,OB,OC,OD,OE;②分别在AO,BO,CO,DO,OE上截取OA′,OB′,OC′,OD′,OE′,使OA′OA=OB′OB=OC′OC=OD′OD=OE′OE=13;③顺次连接A′B′,B′C′,C′D′,D′E′,E′A′.五边形A′B′C′D′E′就是所求作的五边形;(3)画法如下:①分别连接AO,BO,CO,DO,EO,FO并延长;②分别在AO,BO,CO,DO,EO,FO的延长线上截取OA′,OB′,OC′,OD′,OE′,OF′,使OA′OA=OB′OB=OC′OC=OD′OD=OE′OE=OF′OF=12;③顺次连接A′B′,B′C′,C′D′,D′E′,E′F′,F′A′.六边形A′B′C′D′E′F′就是所求作的六边形.方法总结:(1)画位似图形时,要注意相似比,即分清楚是已知原图与新图的相似比,还是新图与原图的相似比.(2)画位似图形的关键是画出图形中顶点的对应点.画图的方法大致有两种:一是每对对应点都在位似中心的同侧;二是每对对应点都在位似中心的两侧.(3)若没有指定位似中心的位置,则画图时位似中心的取法有多种,对画图而言,以多边形的一个顶点为位似中心时,画图最简便.三、板书设计